What is food defence and
vulnerability assessment?

What is food defence and vulnerability
assessment?
What is food defence and vulnerability assessment?
1. Background
As we know BRCGS Global Standard Food Safety Issue 9 has requirements for sites to undertake food defence and vulnerability assessments. These requirements are not new but what is new is that those personnel undertaking food defence and vulnerability assessments have to be trained and have knowledge of both the site and the principles of food defence and vulnerability assessment.
To start we can look at the definitions for food defence and vulnerability assessment:
Food Defence – Also known as Threat Analysis Critical Control Points (TACCP)
Procedures adopted to protect products, premises and brands from malicious actions while under the control of the site
Vulnerability assessment – Also known as Vulnerability Analysis Critical Control Points (VACCP)
Techniques used to identify and mitigate risks associated with raw materials in the supply chain.
HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point)
Keeping food safe from accidental and natural risks to food safety.
We can see from the different definitions that food defence and vulnerability assessment are about intentional malicious contamination which can be ideologically motivated e.g. A person or group motivated by extremist views including religious, political, racist, and single-issue ideologies or for economic gain. Whereas HACCP is to prevent accidental risks to food safety.
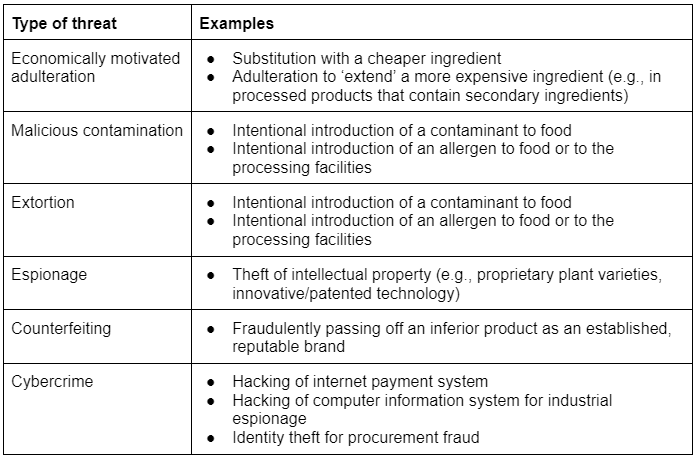
2. Types of threats
PAS 96:2017 provides examples of the type of treats that sites need to be aware of covering:
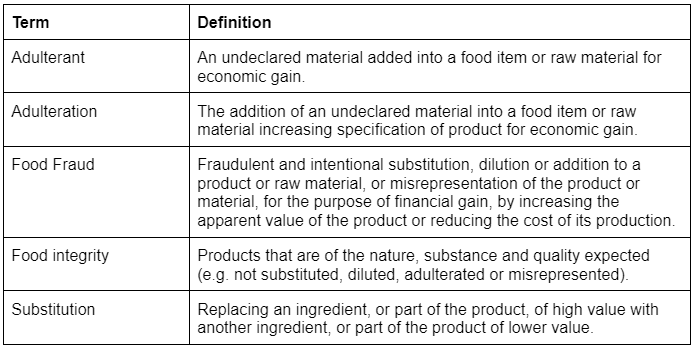
3. Key Terms and definitions
It’s important when undertaking food defence and vulnerability assessment that we understand the differences between the different definitions e.g substitution and adulteration. The definition for substitution is straight forward; “Replacing a high value ingredient with a low value ingredient”. This is generally done for financial gain and a good example is substituting milk with water. There are other reasons why substitution could take place which may revolve around a site not being able to purchase an ingredient and substituting it for a low value ingredient.
Adulteration is a little more complex and is where a fraudster enhances an ingredient or product to make it appear to be higher quality than it actually is. For example adulterating seafood that is going off by spraying it with sanitiser to remove the smell.
Another example is saffron, one of the most frequently adulterated foods. Powdered saffron is more at risk than whole saffron where synthetic dyes are used to boost the colour to a more vibrant yellow.
When setting up a team to undertake food defence or vulnerability assessments it’s important to have people who understand the type of substitutions and adulteration associated with the ingredients and products the site handles.
4. Tools and techniques to undertake food defence and vulnerability assessments
The following details some of the tools and techniques that sites can apply when undertaking a food defence and or vulnerability assessment:
- Horizon Scanning
Is where a company has systems in place for a systematic examination of different information sources to identify potential threats, risks, emerging issues and opportunities.
Typical information may cover:
- Trade associations
- Government sources
- Independent consultants
- Customers
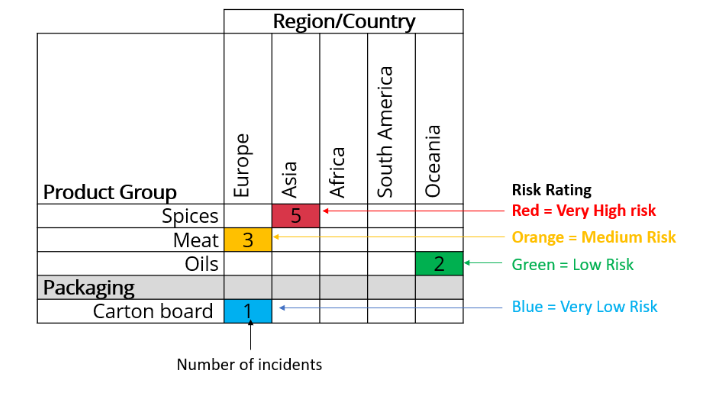
- Risk Maps
A risk map (risk heat map) is a data visualisation tool for communicating specific risks an organisation faces. A risk map helps companies identify and prioritise the risks associated with their business.
5. Supply chain maps
Supply chain mapping (SCM) is the process of documenting information across companies, suppliers, and individuals who are involved in the company’s supply chain, to create a global map of their supply network. For example, documenting the source of material and the different steps it takes to get to site. This allows for the identification of potential substitution and or adulteration at each step in the supply chain.
6. Threat Identification
Information collected from the horizon scanning can then be used to identify potential and actual threats covering:
Adulteration and substitution to purchased raw material and packaging:
- Malicious contamination of ingredients, products and packaging held on site
- Cyber attack
- Counterfeiting
- Extortion
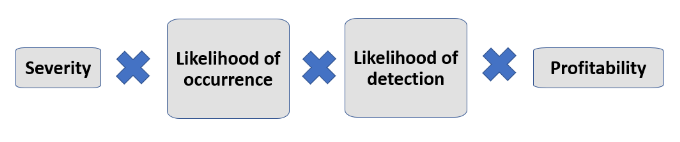
Once the threat analysis has been undertaken then a quantitative risk assessment should be undertaken to allow identified threats to be quantified. Consideration should also be given to the type of risk assessment used e.g Priority Risk Numbers (PRN) where the criteria used to identify threats covers:
Once the identified risks have been quantified they can then be prioritised allowing the appropriate resources to be allocated.
- Mitigation and controls
The food defence and vulnerability assessments then need to review the hierarchy of controls e.g. prevented, eliminated or reduced to acceptable levels. The types of controls a site could apply are:
- Certificates of analysis from raw material suppliers
- Raw material testing
- Supply chain audits
- Use of tamper evidence or seals on incoming raw materials
- Enhance supplier approval checks
- Mass balance exercises at the raw material supplier
- Changes to the supply chain, e.g. a change of supplier or a move to a shorter supply chain
7. Review
The food defence and vulnerability assessment needs to be reviewed annually as a minimum to determine its effectiveness and suitability. In addition the food defence and vulnerability assessment also needs to reviewed when:
- Emergence of a new risk (e.g. publication of information relating to the adulteration of an ingredient).
- Developments in scientific information associated with ingredients, process or product.
- Information received as part of supplier approval or raw material risk assessment which highlights a new or evolving risk
- New raw materials being considered for purchase
- A change in the country of origin or the supplier of raw materials
- A change in the financial situation of the raw material supplier or country of origin
- A change in the cost of raw materials, either upwards or downwards
- A change in the supply chain, logistics and delivery of materials
- A change in availability of the material (e.g. due to seasonal shortages)
If you would like to learn more about food defence and vulnerability assessment and the tools and techniques to undertake assessments then totrain offer a 1 day food defence and vulnerability assessment course. Click here for more information.
Want to learn more about food safety?
About food safety to continually meet regulatory standards? Check out our range of BRCGS and Food Safety and HACCP courses by click on the button below.
tolearn inovative Food Safety Management Platform
Book a tolearn Food Safety Management Management Platform live demo at a date and time which is best for you to see how tolearn can assist your company with onboarding of staff, employee competency and improve food safety culture.